Expert Survey Solutions that deliver.

When you’re dealing with land, whether that’s environmental work, expanding a business or planning a construction project, understanding the different types of land surveys is essential for making informed decisions. Knowing the types of land surveys available to you can offer many benefits. From boundary and topographical surveys to construction and hydrographic surveys, each serves […]
When you’re dealing with land, whether that’s environmental work, expanding a business or planning a construction project, understanding the different types of land surveys is essential for making informed decisions.
Knowing the types of land surveys available to you can offer many benefits. From boundary and topographical surveys to construction and hydrographic surveys, each serves a specific purpose and benefits you at different stages of a project.
RICS-accredited land surveyors can accurately map your properties, confirm legal boundaries and assess construction sites. Their professional guidance ensures your plans meet both legal requirements and practical needs.
Here, we’ll cover the different types of land surveys and how they can benefit businesses, landlords and environmental agencies.
Different types of land surveys help you understand land boundaries, building sizes and landscape features. Accurate survey data supports decisions about property ownership, planning, building design and land management.
A boundary survey determines the exact property boundaries and corners using both physical evidence and legal documents. This survey helps landlords and homeowners know where their land ends and their neighbour’s land begins.
Land surveyors examine deeds, title plans and historical survey records, then measure the land using precise instruments like total stations and GPS. They identify and record boundary monuments such as fences, walls or hedge lines.
If landlords or homeowners face boundary disputes or RoW (right of way) conflict with a neighbour, a boundary survey gives factual evidence to resolve the issue and avoid legal trouble. It is vital for registering land with the Land Registry or updating cadastral records. Landlords may also need this type of land survey when buying, selling or dividing their land.
Typical uses:
A topographical survey maps both natural and artificial topographic features on your property. This includes land elevations, trees, streams, hills and other fixed structures.
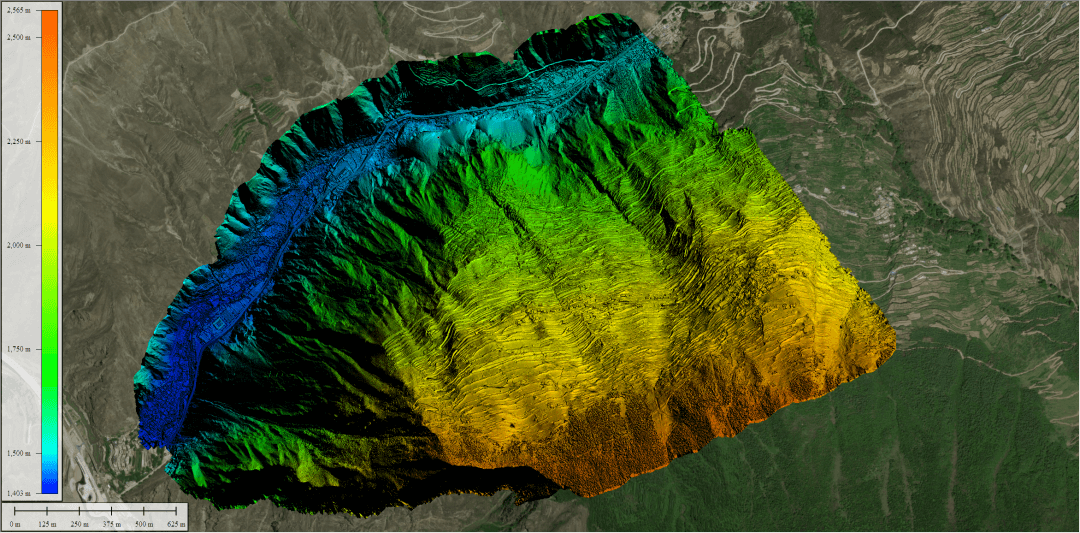
Surveyors use advanced tools like total stations, GNSS (satellite navigation) and drones to create detailed maps in 2D or 3D. Elevation mapping is a key part of this work, showing how the ground rises and falls, and helping businesses plan land development or infrastructure projects.
Accurate topographic data is important for architects, engineers and land managers during the early stages of planning or construction projects. It helps prevent costly surprises and supports better site engineering and design choices.
Advantages include:
A measured building survey records every part of an existing building in detail, both inside and out. This includes the exact positions of walls, windows, doors, staircases, floors, rooflines and sometimes even pipes or cables.
Surveyors use laser scanners to collect data quickly and turn it into floor plans, elevations and digital building models. This type of survey helps you with renovation, extension or restoration projects by giving architects and builders the exact sizes and shapes of rooms and structural elements.
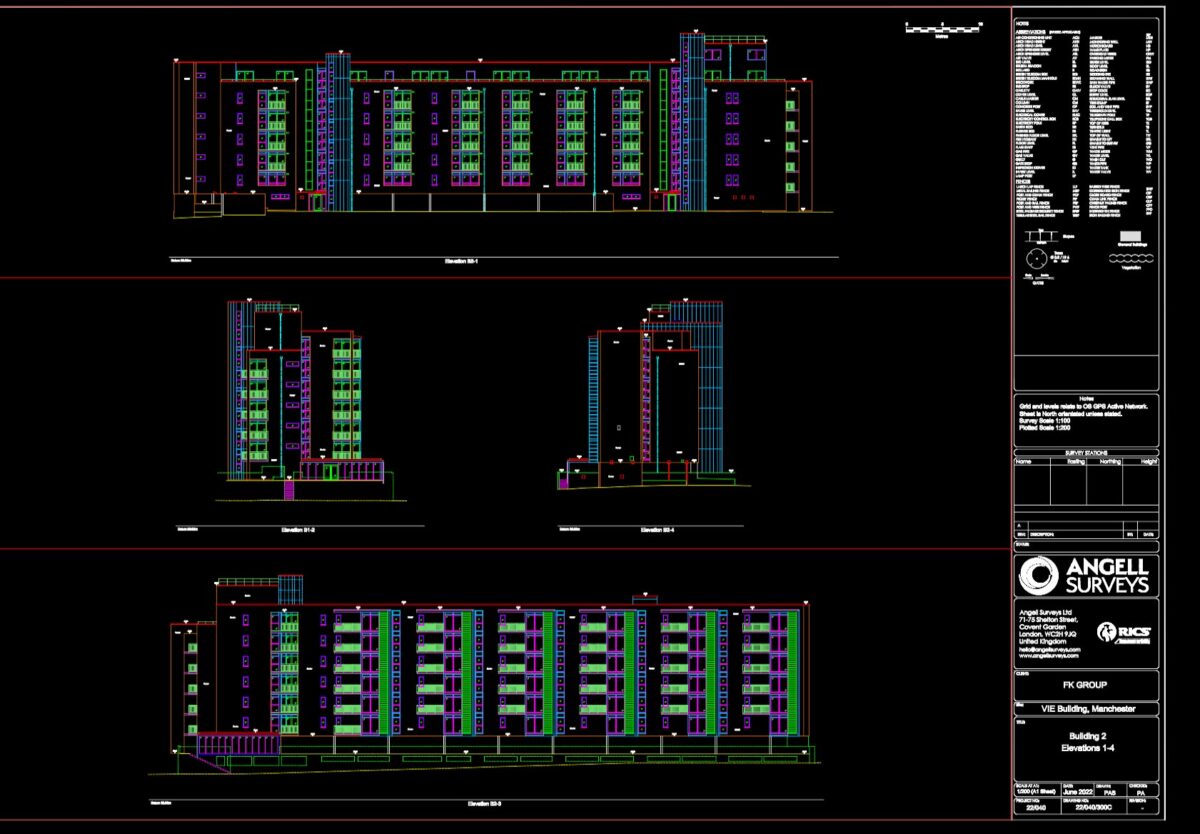
Measured building surveys are needed if you plan to change or extend a property, deal with heritage or listed buildings or need to comply with planning rules. Detailed survey information helps avoid guesswork and costly mistakes.
Key applications include:
New equipment and methods in land surveying mean you can get faster, more accurate site data and insights that weren’t possible before. Sophisticated tools like drones, GNSS receivers, advanced software and 3D laser scanners allow you to map features quickly and assess both above-ground and below-ground conditions with high detail.
Using drones for land surveys has made mapping large or hard-to-reach areas much simpler and quicker. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras, LiDAR and thermal sensors capture aerial photography, ortho imagery and create accurate 2D and 3D maps. You can use drone mapping for digital elevation modelling, volume calculations, construction progress checks and roof inspections.
Drone surveys provide mapping data and geospatial insights that help guide decisions early on, offering centimetre accuracy without needing many people on the ground. This is especially useful for urban planning, infrastructure projects and battery storage sites. BIM and land surveying software process aerial data to create navigation maps or building models and analyse survey points in less time, reducing potential errors and costs.
In construction, surveyors transfer plans onto the ground, setting out exact locations for foundations, roads and buildings using GNSS, total stations and digital levels. Drones make the process easier, faster and safer, with no need for manual mapping onsite. This also reduces safety and injury risks for personnel.
Utility surveys locate underground pipes, cables and other services. Modern surveys take this hazardous — and sometimes impossible — task away from humans and puts them into the capable hands of drones. These devices can fit into areas humans may not be able to, as well as assess dangerous locations. These surveys help prevent accidental damage during excavation or infrastructure projects, improve safety and avoid delays. Construction professionals often rely on detailed mapping services for everything from deviation surveys to rebar surveys.
Soil surveys test the quality, structure and pollution levels in the ground. Knowing soil properties is vital if you want to plan for renewable energy or battery storage, or to meet building regulations for new structures. These surveys help check if the land is stable, safe and suitable for your project.
Subsurface surveys use tools like CCTV drainage surveys, drainage tests and GPR to check the condition and layout of underground pipes, sewers and drainage systems. This helps you quickly find areas needing repair, detect leaks or prevent future flooding problems.
By combining accurate drainage survey results with geospatially related information, you can maintain assets, reduce risk and avoid expensive surprises during construction or property purchase. Services like mobile mapping and 3D laser scanning are now common tools that let you capture three-dimensional objects and environments in great detail for further analysis.

Land surveys use precise methods to define land boundaries, document features and support planning for development projects. They provide the detailed information you need before building or buying land.
In civil engineering, the main types of land surveys include boundary surveys, topographic surveys, construction surveys and subdivision surveys:
A land survey helps you shape your development plans by clearly showing the terrain, property boundaries and existing features. This information is essential for architects and engineers to decide where buildings, roads and utilities should go.
Surveys help you avoid building over legal boundaries or missing important land features, which can save you from legal or financial problems later on. They also identify issues such as uneven land or poor drainage before you start work.
A full land survey report often contains a map with property lines, existing structures, natural features such as streams or trees and measurements showing elevation or slope. The report also notes recorded easements, rights of way and any neighbouring properties that may affect yours. Relevant legal descriptions and references to past deeds or documents are often included as well.
Land surveying is a foundation for safe and legal construction. You cannot place roads, utilities or buildings accurately without clear survey data. Surveyors help translate designs into real-world locations, ensuring that construction follows plan and conforms to regulations.
Land surveys also reduce the risk of mistakes and disputes by providing clear records for all stakeholders during the project.
A topographic survey measures land elevations and records natural and man-made features. Cadastral surveys, often called boundary or property surveys, define the legal property lines and ownership.
Construction surveys mark specific physical locations and reference points on the site for builders to follow. Each type of survey serves a different purpose in the planning and building process.
Trust Angell Surveys for cutting-edge technology, expertise and timely delivery when it matters.